Table of Contents
Short Exam-Oriented Summary
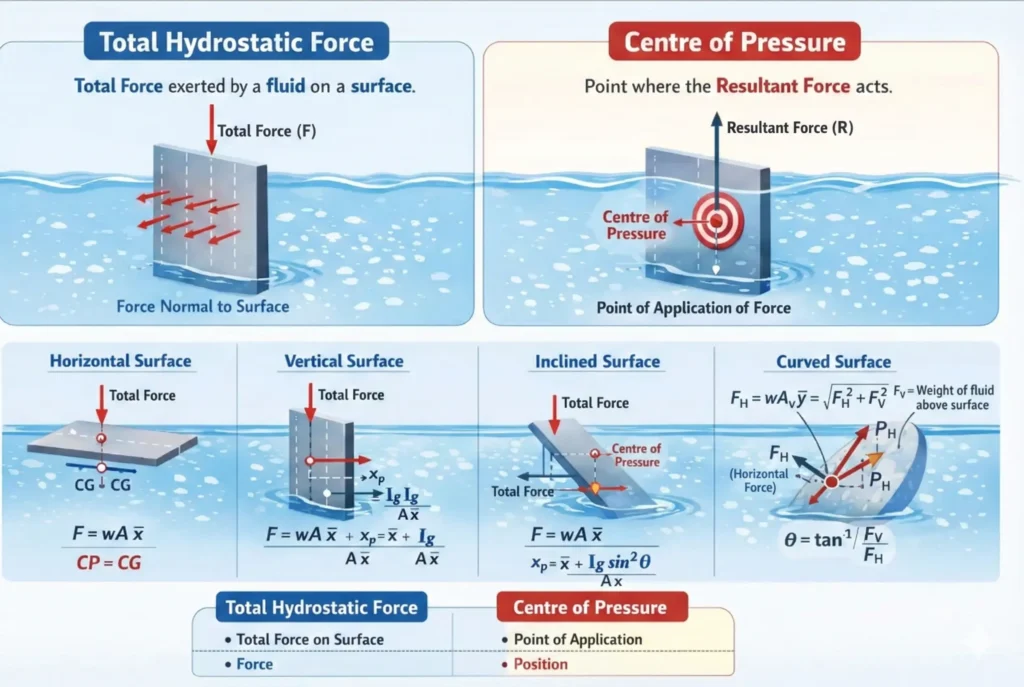
- Total pressure is the total hydrostatic force exerted by a fluid on an immersed surface.
- Centre of pressure is the point where this force acts.
- For horizontal surfaces, centre of pressure = centre of gravity.
- For vertical, inclined, and curved surfaces, centre of pressure lies below the centre of gravity
Definition of Total Pressure
Total pressure is defined as the resultant force exerted by a static fluid on a surface (plane or curved) when the fluid is in contact with that surface.
This force always acts normal (perpendicular) to the surface.
Mathematically, total pressure depends on:
- the specific weight of the liquid,
- the area of the surface, and
- the depth of the surface below the liquid level.
- Also read about the pressure gauge least count
Definition of Centre of Pressure
The centre of pressure is defined as the point of application of the resultant pressure force on an immersed surface.
It is the point where the entire hydrostatic force can be assumed to act.
The centre of pressure does not coincide with the centre of gravity, except in special cases (such as horizontal surfaces), because pressure increases with depth.
Total Pressure and Centre of Pressure on Immersed Surfaces
1. Horizontally Immersed Surface
For a horizontal surface immersed in a liquid:
Total Pressure (P):P=w×A×xˉ
Where:
- w = specific weight of liquid
- A = area of immersed surface
- xˉ = depth of centre of gravity of the surface from liquid surface
✔ This formula is valid for both flat and curved surfaces.
Centre of Pressure:
For a horizontal surface, the centre of pressure coincides with the centre of gravity of the surface.
2. Vertically Immersed Surface
Total Pressure (P):P=w×A×xˉ
Depth of Centre of Pressure (xₚ):xp=xˉ+AxˉIg
Where:
- A = area of the surface
- xˉ = depth of centre of gravity
- Ig = moment of inertia of the surface about its horizontal centroidal axis
3. Inclined Immersed Surface
Total Pressure (P):P=w×A×xˉ
Depth of Centre of Pressure:xp=xˉ+AxˉIgsin2θ
Where:
- θ = angle of inclination of the surface with the liquid surface
4. Curved Immersed Surface
The total force on a curved surface is obtained by resolving it into horizontal and vertical components.
Resultant Force (R):R=PH2+PV2
Direction of Resultant Force:tanθ=PHPV
Where:
- PH = horizontal force = total pressure on the vertical projection of the curved surface
- PV = vertical force = weight of the liquid supported by the curved surface up to the liquid level
Key Difference Between Total Pressure and Centre of Pressure
| Aspect | Total Pressure | Centre of Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Resultant hydrostatic force | Point of application of force |
| Nature | Force quantity | Position/location |
| Depends on | Area, depth, liquid density | Shape, orientation, depth |
| Unit | Newton (N) | Metre (m) |
