On this page we will go through the following:
The lathe machine is a very important part of any manufacturing industry, There’s a saying that the Lathe machine is the mother of all machines because it is the reason for the inventions of a lot of well-known machines in history and the wide range of operations that can be performed on the machines is incredible that it is still in use with upgraded version.
What is a lathe machine?
A lathe machine is a machine tool used to rotate a workpiece about its axis while a cutting tool is applied against it to remove material and shape it into the desired form. It is primarily used for operations such as turning, facing, threading, drilling, and knurling, making it one of the most essential machines in metalworking and manufacturing industries.
In simple terms,
A lathe machine works by rotating the workpiece while the cutting tool shapes it into a precise cylindrical or conical form.
Lathe machine diagram
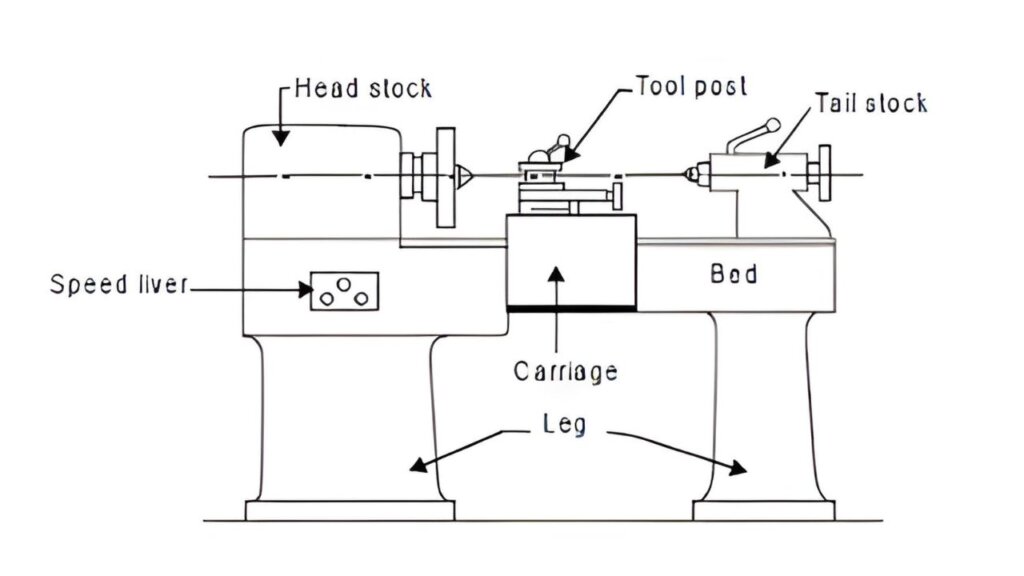
Also Read:
1) 10 of the Most Popular Types of Lathe Machine Jobs in 2025
2) Indemand 18 Product Ideas to Make on a Lathe Machine and Earn
10 Main Parts of lathe machine
A lathe machine consists of several important parts that work together to perform various machining operations such as turning, facing, drilling, and threading. Each part has a specific function that ensures accuracy, stability, and smooth operation.
In summary:
The main parts of a lathe machine include the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, cross-slide, compound rest, apron, lead screw, chuck, and tool post, all working together to shape materials accurately and efficiently.
Detailed overview of 10 Main Parts of lathe machine
- Bed:
The bed is the base of the lathe machine, providing support, alignment, and rigidity for all other components. It ensures the stability of the entire machine during operation. - Headstock:
The headstock is mounted on the left side of the bed. It houses the spindle and gearbox, which are responsible for holding and rotating the workpiece at different speeds. - Tailstock:
Located on the opposite end of the headstock, the tailstock supports the free end of the workpiece. It can also hold a drill chuck or center for operations like drilling or reaming. - Carriage:
The carriage moves longitudinally along the bed and carries the cutting tool. It enables the tool to feed against the rotating workpiece. - Cross-Slide:
The cross-slide moves perpendicular to the lathe bed, allowing the operator to control the cutting depth and position the tool accurately. - Compound Rest:
The compound rest supports the tool post and can be swiveled at an angle, making it useful for taper turning or angular cuts. - Apron:
Attached to the front of the carriage, the apron contains the gears and mechanisms that control the movement of the carriage and cross-slide. - Lead Screw:
The lead screw is a long threaded shaft that transmits power to move the carriage precisely during thread-cutting operations. - Chuck:
The chuck is a clamping device fitted on the spindle that holds and rotates the workpiece securely. - Tool Post:
The tool post is mounted on the compound rest and holds various cutting tools for performing different machining operations.
Lathe machine diagram with all parts
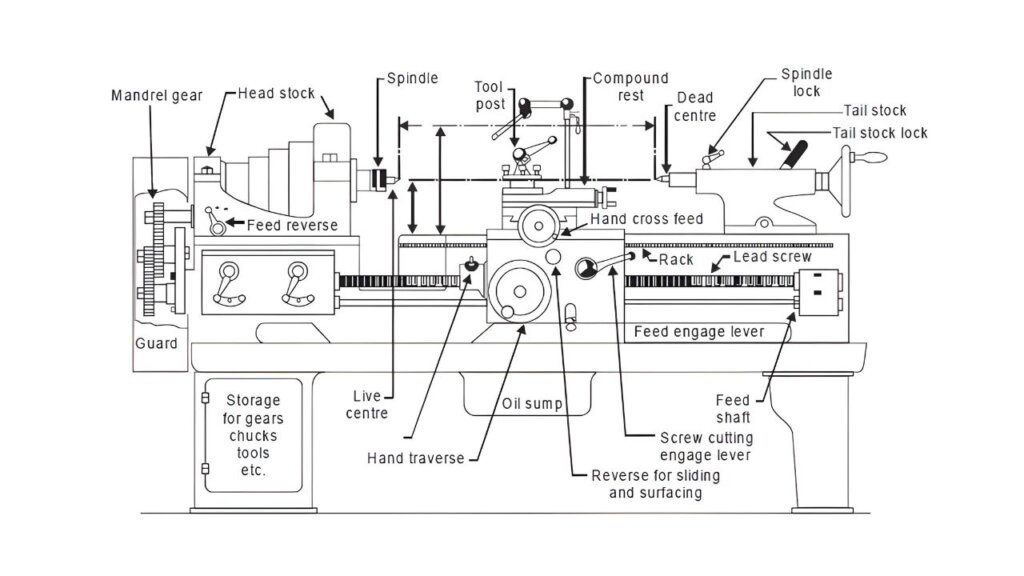
Working principle of Lathe machine:
The working principle of a lathe machine is based on the concept of rotating the workpiece against a fixed cutting tool. In this process, the workpiece is securely mounted on the spindle, which rotates it at a controlled speed. The cutting tool, held firmly in the tool post, is fed either longitudinally (along the length) or transversely (across the diameter) of the rotating workpiece.
As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool removes excess material in the form of chips to produce the desired shape, size, and surface finish. By carefully adjusting the Cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut, the operator can perform a variety of operations such as turning, facing, knurling, grooving, threading, and drilling.
In simple terms,
A lathe machine works on the principle of rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool is moved against it to remove material and form the required shape.
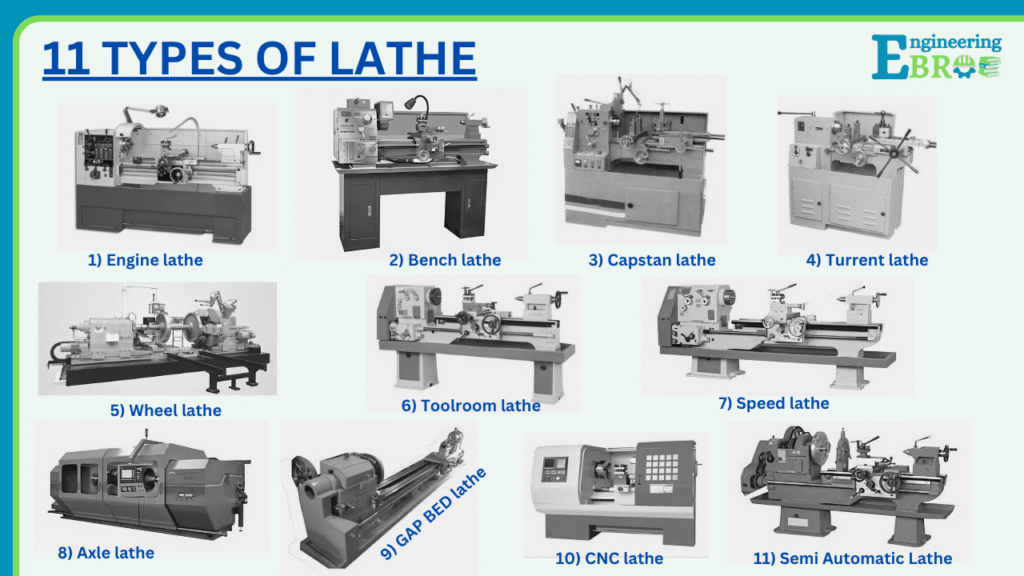
7 types of lathe machines:
Lathe machines are used for shaping, cutting, and finishing materials like metal, wood, and plastic. Types of lathe include the following
- Speed lathe
- Engine lathe
- Bench lathe
- Toolroom lathe
- Turrent lathes
- Special Purpose lathes
- Automatic lathe or CNC lathe
Also Read: Indemand 18 product ideas to make on a lathe machine and earn
11 Types of Lathe machine operations:
- 11 Types of lathe machine operations
A lathe machine can perform a wide range of operations to shape and finish metal or wood workpieces. These operations are classified based on the type of cutting and the purpose of machining. The main types of lathe machine operations are listed below:
In summary:
The main types of lathe machine operations include turning, facing, drilling, knurling, chamfering, forming, threading, and miscellaneous operations, each designed to remove material in a controlled way to achieve precise shapes and finishes.
Detailed overview of Main Types of lathe machine operations
- Turning Operation:
In this operation, the cutting tool removes material from the outer surface of a rotating workpiece to produce a cylindrical shape. It helps reduce the diameter and achieve smooth finishes. - Facing Operation:
Facing is used to produce a flat surface at the end of a workpiece by moving the cutting tool perpendicular to the lathe’s axis of rotation. - Drilling Operation:
A drilling tool is fed into the rotating workpiece to create a hole along its axis using a drill bit mounted in the tailstock. - Knurling Operation:
This operation is performed to create a rough or patterned surface on the workpiece for better grip or decorative purposes using a knurling tool. - Chamfering Operation:
Chamfering involves cutting the edge of a cylindrical workpiece at a specific angle to remove sharp edges and improve aesthetics. - Forming Operation:
A specially shaped cutting tool is used to reproduce a particular contour or profile on the workpiece surface. - Threading Operation:
In threading, a tool is moved longitudinally along the rotating workpiece to cut helical grooves, producing external or internal threads. - Miscellaneous Operations:
Other operations such as grooving, boring, parting-off, polishing, and taper turning are also performed on a lathe to achieve specific machining requirements.

How to decide which type of lathe is suitable for you?
If you are someone who wants to buy a lathe for yourself then we suggest you check the following specifications of the machine, make sure you know what product size you will manufacture on the lathe, before you see these specifications
Specifications of lathe
- Swing Over Bed: Typically ranges from 8 inches to over 60 inches, indicating the maximum diameter of the workpiece that can be accommodated on the lathe.
- Distance Between Centers: Usually specified in inches or millimeters, representing the maximum length of the workpiece that can be held between the lathe’s centers.
- Spindle Speed: Denoted in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicating the range of rotational speeds the lathe can achieve. Higher speeds allow for a wider range of machining operations.
- Bed Length: Length of the lathe bed, providing support to the carriage and tailstock. Longer beds accommodate larger workpieces and provide better stability during machining.
- Motor Power: Expressed in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), indicating the power output of the lathe’s motor. Higher power allows for machining of tougher materials and larger workpieces .
- Spindle Bore Diameter: Diameter of the hole through the spindle, determining the maximum diameter of the workpiece that can be passed through the spindle for machining .
- Tailstock Quill Diameter and Travel: Diameter of the quill on the tailstock and the distance it can travel, which affects the support and centering of long workpieces.
- Threading Capabilities: Specifies the range of thread pitches that can be cut on the lathe, often expressed in threads per inch (TPI) or millimeters per revolution (mm/rev) .
- Overall Dimensions and Weight: Indicates the physical size and weight of the lathe, important for space considerations and transportation
FAQs – Lathe machine
1. What is a lathe machine used for?
A lathe machine is used to shape, cut, drill, thread, or finish a rotating workpiece. It is widely used in metalworking and manufacturing industries to produce cylindrical, conical, or complex shapes with high accuracy.
2. Why is the lathe called the mother of all machines?
The lathe is called the mother of all machines because it is the first machine tool invented and forms the basis for the creation of many other machines. It is versatile and capable of performing a wide range of operations.
3. What are the main parts of a lathe machine?
The main parts of a lathe machine include the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, cross-slide, compound rest, apron, lead screw, chuck, and tool post. Each part has a specific function to ensure accuracy, stability, and smooth operation.
4. How does a lathe machine work?
A lathe machine works by rotating the workpiece about its axis while a cutting tool is fed against it to remove material. The feed, speed, and depth of cut are controlled to achieve the desired shape, size, and surface finish.
5. What are the different types of lathe machines?
Common types of lathe machines include speed lathe, engine lathe, bench lathe, toolroom lathe, turret lathe, capstan lathe, CNC lathe (automatic or semi-automatic), gap bed lathe, wheel lathe, and axle lathe. Each type is designed for specific machining needs.
6. What operations can be performed on a lathe machine?
A lathe machine can perform operations such as turning, facing, drilling, knurling, chamfering, forming, threading, and other miscellaneous operations like grooving, parting-off, and taper turning.
7. How to choose the right lathe machine?
When selecting a lathe machine, consider swing over bed, distance between centers, spindle speed, bed length, motor power, spindle bore diameter, tailstock quill diameter, threading capabilities, and overall dimensions based on the size and type of workpieces you plan to manufacture.
8. What is the difference between CNC lathe and manual lathe?
A CNC lathe is computer-controlled, offering precise, automated operations, while a manual lathe requires the operator to control the movement of the cutting tool and workpiece manually. CNC lathes are ideal for high-volume production with consistent quality.
9. What is the importance of the lathe’s lead screw?
The lead screw transmits motion from the carriage drive system to enable precise thread cutting and synchronized movement of the cutting tool along the bed.
10. Can a lathe machine be used for both metal and wood?
Yes, certain lathe machines are designed for metalworking, while others, like wood lathes, are specially made for shaping wood. However, metal lathes can also be used for hard plastics and similar materials.