A Vernier height gauge is a precision measuring instrument widely used in workshops, engineering labs, and manufacturing units to measure the vertical height of objects. Whether you are inspecting a machined part or marking a layout, the Vernier height gauge ensures high accuracy.
Understanding the Vernier height gauge least count is essential because it determines the smallest measurement the instrument can read, directly affecting precision. In this guide, you will learn what least count is, how to calculate it, and how to use a Vernier height gauge correctly.
Also read: Vernier Caliper detailed guide
Table of Contents
What is a Vernier Height Gauge?
The Vernier height gauge consists of a main vertical scale, a sliding Vernier scale, a measuring jaw or scriber, and a base. It measures height from a reference plane and is commonly used on surface plates.
Key Features:
- Measures vertical heights with high accuracy
- Allows scribing lines for layout purposes
- Available in multiple sizes and types
Parts of a Vernier Height Gauge
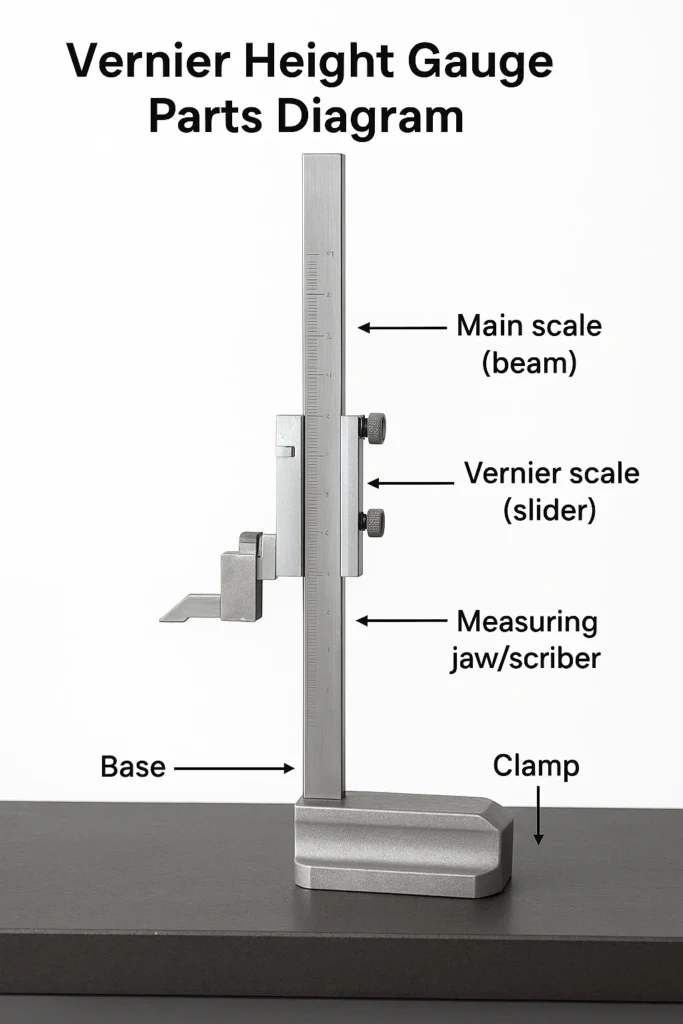
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Base | Provides a stable reference plane for measurements |
| Main Scale (Beam) | Vertical bar with engraved measurements |
| Vernier Scale (Slider) | Sliding scale for precise readings |
| Measuring Jaw/Scriber | Marks or contacts the surface |
| Fine Adjustment Screw | Enables small, precise movements |
| Clamp | Locks the slider in position to avoid errors |
Pro Tip: Always clean the base and surface plate before using the gauge to avoid inaccurate readings.
What is Least Count?
Least count (LC) is the smallest measurement that an instrument can reliably read. It defines the precision of the Vernier height gauge.
Formula for Vernier Height Gauge:
Least Count= 1 Main Scale Division − 1 Vernier Scale Division
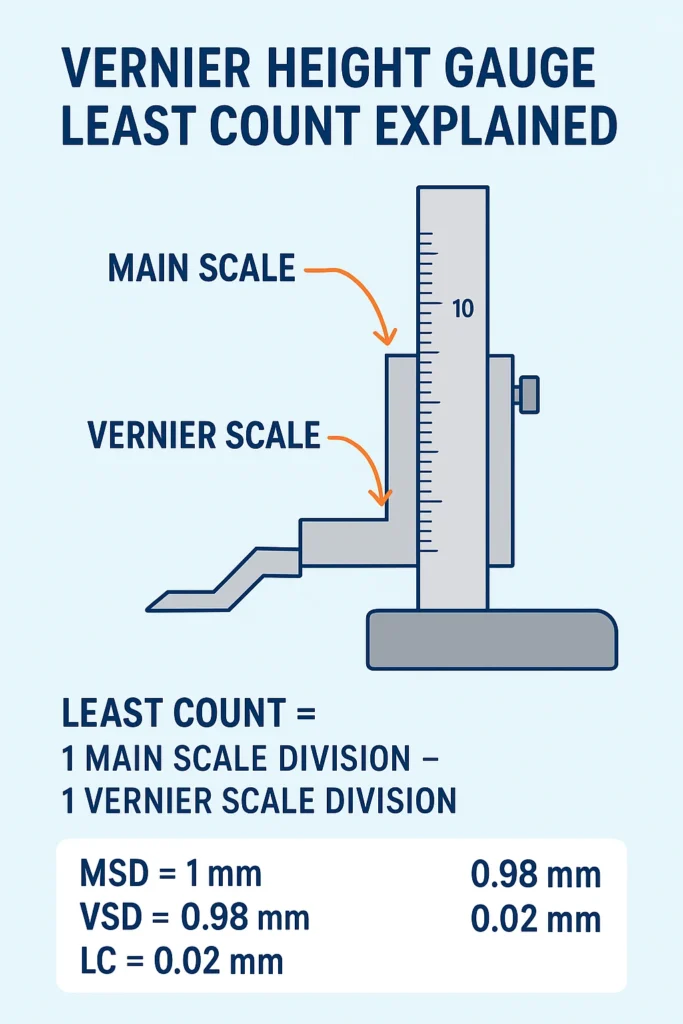
Example Calculation:
- Main Scale Division (MSD) = 1 mm
- Vernier Scale Divisions = 50 divisions equal to 49 mm on the main scale
- Vernier Scale Division (VSD) = 49 ÷ 50 = 0.98 mm
- Least Count = 1 − 0.98 = 0.02 mm
✅ This means the smallest height measurable by the Vernier height gauge is 0.02 mm.
Tip: You cannot measure a height smaller than the least count.
How to Measure with a Vernier Height Gauge
- Place the Vernier height gauge on a clean surface plate.
- Loosen the slider clamp and move the measuring jaw near the object.
- Tighten the clamp for stability.
- Align the Vernier scale to take a precise reading.
- Add the main scale reading and Vernier scale reading for total height.
Example:
- Main scale reading = 12 mm
- Vernier scale reading = 0.14 mm
- Total measurement = 12.14 mm
Types of Height Gauges
| Type | Least Count | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vernier | 0.02 mm | Durable, simple | Requires skill to read |
| Dial | 0.01 mm | Easier reading | Mechanical wear possible |
| Digital | 0.01 mm | Quick, clear | Expensive, needs battery |
| Electronic | 0.001 mm | Highly precise | Needs calibration & power |
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
- Parallax Error: Always read the scale straight from the front.
- Surface Plate Dirt: Clean the plate before measurement.
- Base Flexing: Ensure base is proportional to vertical beam.
- Excessive Pressure: Avoid pressing the scriber too hard.
- Temperature Effects: Keep the gauge at room temperature for accuracy.
Tips for Accurate Measurements
- Check zero reading before each measurement.
- Use the fine adjustment screw for precise alignment.
- Avoid sudden movements or dropping the gauge.
- Store the gauge in a low-humidity environment and lubricate lightly with rust-preventive oil.
- Regular calibration ensures consistent accuracy.
FAQs
Q1: What is the least count of a Vernier height gauge?
A: The least count of a vernier height gauge is 0.02 mm, depending on the manufacturer, model and type it could vary
Q2: Can Vernier height gauge measure in inches?
A: Yes, some models provide dual scales in mm and inches.
Q3: How to improve precision with a Vernier height gauge?
A: Use a clean surface plate, proper alignment, and fine adjustment screws.
Q4: Difference between Vernier and digital height gauge?
A: Vernier requires reading lines manually; digital displays the measurement on a screen with higher ease and speed.
Conclusion
The Vernier height gauge least count is the foundation of precise vertical measurements in workshops and engineering labs. Understanding parts, least count, proper measurement technique, and error prevention ensures high accuracy. With careful handling and regular calibration, a Vernier height gauge can consistently deliver measurements accurate to 0.02 mm, making it indispensable for precision work.