What is a Thermal power plant?
The thermal power plant is defined as a system that converts Heat Energy to Electrical Energy, and also it is a collective term of various power plants such as Coal power plant, Nuclear Power plants, Solar power plant, Geothermal power plant and more but Coal power plant is considered as Thermal power plant
Table of Contents
Introduction
In this blog, we will learn about Thermal power plant, the Components, working, about the thermodynamic cycle , and a few extra things,
ALSO READ:
Rankine cycle comprehensive guide (Thermal power plant works in rankine cycle)
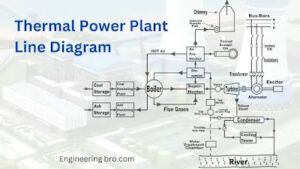
Components of Thermal power plant
There are a lot of components a Coal power plant (Thermal power plant) has but here is the list of components that must be included
Boiler
A Boiler is a critical component that generates high-temperature steam by heating water using a heat source, such as coal, natural gas, or nuclear reactions.
The boiler’s function is to efficiently transfer heat energy from the fuel source to the water, enabling the conversion of thermal energy into mechanical energy and eventually electrical power.
Turbine
A Turbine is a device that converts the high-pressure, high-temperature steam generated in the boiler into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to drive a generator, which ultimately produces electricity.
Generator
A generator in a power plant converts mechanical energy from a steam turbine into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction, supplying electricity to the grid.
Condensor
A condenser in a power plant is a heat exchanger device that plays a crucial role in converting steam used to drive turbines back into liquid water for reuse. It transfers heat from the steam to a cooling medium (usually water or air) in order to facilitate efficient and continuous power generation.
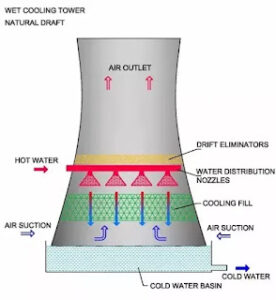
Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a heat exchange system that removes excess heat from industrial processes by evaporating water, ensuring equipment efficiency and safe operation.
It is a structure that uses evaporation to cool water used in industrial operations, preventing equipment overheating and maintaining optimal working conditions.
Ash control system
The ash control system in a power plant manages the collection, disposal, and utilization of ash generated from the combustion of coal or other fuels, ensuring environmental compliance and resource efficiency. It encompasses techniques and equipment for ash handling, storage, and potential reuse.
Coal control system
The coal control system in a thermal power plant regulates the supply, storage, and distribution of coal to the boilers, ensuring efficient and consistent combustion for electricity generation. It encompasses monitoring, automation, and coordination of coal handling processes to optimize power plant performance.
Chimney
A chimney is a tall vertical structure that exhausts flue gases and particulate matter produced during the combustion of fuels, effectively venting them into the atmosphere while minimizing environmental impact.
Water Treatment plant
A water treatment plant is a facility that purifies and conditions water used in various processes, such as steam generation and cooling, to ensure proper equipment function and minimize potential environmental effects through effective filtration, chemical treatment, and purification methods.
A few Extra Components which increases the efficiency of power plant are as follows
Economiser
An economizer is a heat exchanger device that preheats the feedwater by recovering heat from the flue gases leaving the boiler.
Air preheater
An air preheater is a heat exchange component that warms the combustion air by utilizing waste heat from the flue gases.
Superheater
A superheater is a heat exchanger section that raises the temperature of steam produced in the boiler, improving its thermal energy content
Draught fans
Draught fans are mechanical devices that create and control airflow within the combustion process, ensuring proper ventilation, efficient fuel combustion, and effective heat transfer in boilers and furnaces.
Working of a Thermal power plant
1. Fuel Combustion: Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) are burned to produce high-temperature gases.
2. Boiler: Heat from combustion gases is used to raise water temperature and pressure in a boiler.
3. Steam Turbine: High-pressure steam from the boiler turns turbine blades.
4. Turbine Rotation: Turbine’s spinning motion drives a generator.
5. Generator: Mechanical energy from the turbine is converted into electricity.
6. Condenser: Steam is cooled and condensed back into water in a heat exchanger.
7. Cooling System: Cooling medium (water or air) removes excess heat.
8. Feedwater Heater: Some plants preheat water using condensed steam’s heat.
9. Electrical Transmission: Generated electricity is transformed and sent through power lines.
This process converts heat energy from burning fossil fuels into electrical energy for widespread use.
FAQs
Thermal power plants work on which cycle?
Thermal power plants typically work on the Rankine cycle.
How many thermal power plants are there in India?
There were around 229 according to 2021 reports, thermal power plants in India. However, this number might have changed since then due to new plant constructions or closures.
India’s 1st Thermal power plant was?
Hussain Sagar thermal power plant was the 1st Thermal power plant which was located in Hyderabad later demolished